Abstract
Research Article
Forensic Comparison of Textile Fibre for Identification using X-ray Diffraction Technique
MC Janaki* and S Anil Kumar
Published: 19 December, 2023 | Volume 7 - Issue 1 | Pages: 083-088
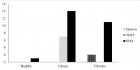
This study delves into the forensic examination of textile fibers for identification through the application of the X-ray diffraction (XRD) technique. With the textile industry producing an array of materials, both natural and man-made fibers, the need to distinguish between them for forensic purposes becomes paramount. The primary objective of this research is to identify unique characteristics in fiber samples, differentiating between branded and non-branded company textiles. The focus is placed on fresh, unused cloth fibers obtained directly from shops. The study encompasses two broad categories of fibers: natural (such as cotton, silk, and wool) and man-made (including nylon, rayon, and polyester). Samples from both branded and non-branded textiles undergo analysis using XRD, a sophisticated method capable of revealing the crystallographic structure of materials. Results obtained from the XRD analysis unveil intensity peaks at various levels and degrees, providing distinctive patterns for individualization. Even within the same fiber category, such as polyester and cotton, discernible differences in intensity peaks facilitate the identification process. This research contributes to the advancement of forensic techniques by offering a reliable means of identifying textile fibers. The utilization of XRD not only allows for the differentiation between natural and man-made fibers but also enables discrimination among textiles produced by different companies. The implications of this study extend to forensic investigations, where the ability to precisely identify fibers can provide valuable evidence in criminal cases involving textiles.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001055 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Textile; Fibre; Crystalline; Cotton; Polyester; X-ray Diffraction
References
- Farah S, Kunduru KR, Tsach T, Bentolila A, Domb AJ. Forensic comparison of synthetic fibers. Polymers for Advanced Technologies. 2015; 26(7): 785–796. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.3540
- Aljannahi A, Alblooshi RA, Alremeithi RH, Karamitsos I, Ahli NA, Askar AM, Albastaki IM, Ahli MM, Modak S. Forensic Analysis of Textile Synthetic Fibers Using a FT-IR Spectroscopy Approach. Molecules. 2022 Jul 3;27(13):4281. doi: 10.3390/molecules27134281. PMID: 35807525; PMCID: PMC9268719.
- Powell R, Collins P, Horsley G, Coumbaros J, van Bronswijk W. Enhancing the evidential value of textile fibres Part 2: Application of a database-driven fibre comparison strategy to a cold-case investigation. Forensic Sci Int. 2021 Aug;325:110894. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2021.110894. Epub 2021 Jul 2. PMID: 34271326.
- Meleiro PP, García-Ruiz C. Spectroscopic techniques for the forensic analysis of textile fibers. Applied Spectroscopy Reviews. 2016; 51(4): 278–301. https://doi.org/10.1080/05704928.2015.1132720
- Mujumdar N, Campiglia AD. CHAPTER 7. A Review on Analytical Techniques Used for Forensic Fiber Analysis. In G Miolo, JL Stair, M Zloh (Eds.), Comprehensive Series in Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences. Royal Society of Chemistry. 2018; 175-206. https://doi.org/10.1039/9781788010344-00175
- Peets, P., Kaupmees, K., Vahur, S., & Leito, I. (2019). Reflectance FT-IR spectroscopy as a viable option for textile fiber identification. Heritage Science, 7(1), 93. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40494-019-0337-z
- Peets, P., Leito, I., Pelt, J., & Vahur, S. (2017). Identification and classification of textile fibres using ATR-FT-IR spectroscopy with chemometric methods. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 173, 175–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2016.09.007
- Zapata, F., Ortega-Ojeda, F. E., & García-Ruiz, C. (2022). Forensic examination of textile fibres using Raman imaging and multivariate analysis. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 268, 120695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120695
- Wang C, Wang N, Liu S, Simth LLP, Zhang H, Zhi Z. Investigation of Microfibril Angle of Flax Fibers Using X-Ray Diffraction and Scanning Electron Microscopy. Journal of Natural Fibers. 2020; 17(7): 1001-1010. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2018.1546639
- Schotman TG, Xu X, Rodewijk N, van der Weerd J. Application of dye analysis in forensic fibre and textile examination: Case examples. Forensic Sci Int. 2017 Sep;278:338-350. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2017.07.026. Epub 2017 Jul 31. PMID: 28802950.
- Goodpaster JV, Liszewski EA. Forensic analysis of dyed textile fibers. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009 Aug;394(8):2009-18. doi: 10.1007/s00216-009-2885-7. Epub 2009 Jun 20. PMID: 19543886.
- Śmigiel-Kamińska D, Pośpiech J, Makowska J, Stepnowski P, Wąs-Gubała J, Kumirska J. The Identification of Polyester Fibers Dyed with Disperse Dyes for Forensic Purposes. Molecules. 2019 Feb 10;24(3):613. doi: 10.3390/molecules24030613. PMID: 30744148; PMCID: PMC6384617.
- Śmigiel-Kamińska D, Wąs-Gubała J, Stepnowski P, Kumirska J. The Identification of Cotton Fibers Dyed with Reactive Dyes for Forensic Purposes. Molecules. 2020 Nov 20;25(22):5435. doi: 10.3390/molecules25225435. PMID: 33233593; PMCID: PMC7699748.
- Liang J, Frazier J, Benefield V, Chong NS, Zhang M. Forensic Fiber Analysis by Thermal Desorption/Pyrolysis-Direct Analysis in Real Time-Mass Spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2020 Jan 21;92(2):1925-1933. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04167. Epub 2019 Dec 31. PMID: 31846295.
- Lynch BJ, Kerrigan GC. Identification of single fibres by X‐ray diffraction in forensic analysis. X-Ray Spectrometry. 1981;10(4): 196-197. https://doi.org/10.1002/xrs.1300100411
- Mihajlović RA. The Use of X-ray Diffraction Analysis in Different Forensic Disciplines. In W. E. Lee, R. Gadow, V. Mitic, & N. Obradovic (Eds.), Proceedings of the III Advanced Ceramics and Applications Conference. 2016; 353-359. Atlantis Press. https://doi.org/10.2991/978-94-6239-157-4_24
- Williams GA. Forensic textile damage analysis: Recent advances. Research and Reports in Forensic Medical Science. 2018; 8: 1-8. https://doi.org/10.2147/RRFMS.S166435
- Raven MD, Fitzpatrick RW, Self PG. Trace evidence examination using laboratory and synchrotron X-ray diffraction techniques. Geological Society, London. Special Publications. 2021; 492(1): 165-179. https://doi.org/10.1144/SP492-2019-36
- Galais V, Fleming H, Nic Daéid N, Ménard H. Scientometric analysis of the forensic science literature for fibre as an evidence type: Access and data availability. Forensic Sci Int Synerg. 2022 May 17;5:100269. doi: 10.1016/j.fsisyn.2022.100269. PMID: 35634573; PMCID: PMC9133568.
- Nishiwaki Y, Honda S, Yamato T, Kondo R, Kaneda A, Hayakawa S. Nondestructive Differentiation of Polyester Single White Fibers Using Synchrotron Radiation Microbeam X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry with Vertical Focusing. J Forensic Sci. 2020 Sep;65(5):1474-1479. doi: 10.1111/1556-4029.14481. Epub 2020 Jun 15. PMID: 32539170.
- Deng X, Ye S, Wan L, Wu J, Sun H, Ni Y, Liu F. Study on Dissolution and Modification of Cotton Fiber in Different Growth Stages. Materials (Basel). 2022 Apr 6;15(7):2685. doi: 10.3390/ma15072685. PMID: 35408020; PMCID: PMC9000360.
Figures:

Figure 1

Figure 2

Figure 3

Figure 4
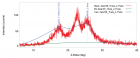
Figure 5
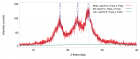
Figure 6
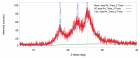
Figure 7

Figure 8
Similar Articles
-
Sensitivity and Intertextile variance of amylase paper for saliva detectionAlexander Lotozynski*. Sensitivity and Intertextile variance of amylase paper for saliva detection. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001017; 4: 001-003
-
Forensic Comparison of Textile Fibre for Identification using X-ray Diffraction TechniqueMC Janaki*,S Anil Kumar. Forensic Comparison of Textile Fibre for Identification using X-ray Diffraction Technique. . 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001055; 7: 083-088
Recently Viewed
-
Metastatic Brain Melanoma: A Rare Case with Review of LiteratureNeha Singh,Gaurav Raj,Akshay Kumar,Deepak Kumar Singh,Shivansh Dixit,Kaustubh Gupta*. Metastatic Brain Melanoma: A Rare Case with Review of Literature. J Radiol Oncol. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jro.1001080; 9: 050-053
-
Validation of Prognostic Scores for Attempted Vaginal Delivery in Scar UterusMouiman Soukaina*,Mourran Oumaima,Etber Amina,Zeraidi Najia,Slaoui Aziz,Baydada Aziz. Validation of Prognostic Scores for Attempted Vaginal Delivery in Scar Uterus. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001185; 8: 023-029
-
Scientific Analysis of Eucharistic Miracles: Importance of a Standardization in EvaluationKelly Kearse*,Frank Ligaj. Scientific Analysis of Eucharistic Miracles: Importance of a Standardization in Evaluation. J Forensic Sci Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001068; 8: 078-088
-
A study of coagulation profile in patients with cancer in a tertiary care hospitalGaurav Khichariya,Manjula K*,Subhashish Das,Kalyani R. A study of coagulation profile in patients with cancer in a tertiary care hospital. J Hematol Clin Res. 2021: doi: 10.29328/journal.jhcr.1001015; 5: 001-003
-
Additional Gold Recovery from Tailing Waste By Ion Exchange ResinsAshrapov UT*, Malikov Sh R, Erdanov MN, Mirzaev BB. Additional Gold Recovery from Tailing Waste By Ion Exchange Resins. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001098; 7: 132-138
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."