Abstract
Research Article
Comparative analysis of mobile forensic proprietary tools: an application in forensic investigation
Parth Chauhan*, Tamanna Jaitly and Animesh Kumar Agrawal
Published: 22 November, 2022 | Volume 6 - Issue 1 | Pages: 077-082
The utilization of the Internet and wireless communication reaches its pinnacle from one side of the planet to the other. Marking the rise of criminal activity in recent years sees enormous growth in security breaches and data theft-related cases in mobile phones. To mitigate them, the implementation of security patches, safety fixes, and updates in mobile devices is of high priority for the organization. The need to foster techniques and procedures in the field to be able to extract and precisely dissect digital crime cases, providing valuable tactical data about the investigation. Mobile forensics is a developing branch assisting the investigator in criminal trials and investigations. Acquisition, Collection, and Analysis of mobile phones settle the purpose of recovering cumulative and corroborative evidence. Upgradation and innovation of mobile devices with time imposed a challenge to mobile forensic technology to extract information from such devices. The study aims at extracting comparative and statistical approaches in the analysis of Physical data acquisition utilizing significant versatile mobile criminological proprietary tools. The proposed study also introduces newly developed utility tools along with their characteristic features which help in successful data extraction from mobile devices.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001039 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Security breach; Mobile forensic; Acquisition; Cumulative evidence; Corroborative evidence and Data extraction
References
- Simon K, Pte K. Ltd. https://datareportal.com/reports/digital-2022-global-overview-report
- Lahesoo P, Mäses S. Forensic Traces of Messaging Applications on Android and iOS Mobile phones.
- Umar R, Riadi I, Zamroni GM. Mobile forensic tools evaluation for digital crime investigation. Int J Adv Sci Eng Inf Technol. 2018; 8(3): 949.
- Osho O, Ohida SO. Comparative evaluation of mobile forensic tools. IJ Inf. Technol. Comput. Sci. 2016; 1:74-83.
- Sinha R, Sihag V, Choudhary G, Vardhan M, Singh P. Forensic Analysis of Fitness Applications on Android. In the International Symposium on Mobile Internet Security 2021; 222:235.
- Aljahdali A, Alsaidi N, Alsafri M, Alsulami A, Almutairi, T. Mobile device forensics. Romanian Journal of Information Technology and Automatic Control. 2021; 31(3): 81-96.
- Eriş FG, Akbal E. Forensic Analysis of Popular Social Media Applications on Android Smartphones. Balkan Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering. 2021; 9(4):386-397.
- Dasgupta RK. Mobile forensic: Investigation of dead or damaged smartphone-An overview, tools and technique challenges from law enforcement perspective. Research gate Journal. 2021. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Rhythm-Dasgupta/publication/340939977_Mobile_Forensic_Investigation_of_Dead_or_Damage_Smart_Phone_-An_Overview_Tools_Technique_Challenges_from_Law_Enforcement_Perspective/links/5ea68b62299bf11256128683/Mobile-Forensic-Investigation-of-Dead-or-Damage-Smart-Phone-An-Overview-Tools-Technique-Challenges-from-Law-Enforcement-Perspective.pdf
- Agrawal AK, Sharma A, Sinha SR, Khatri P. Forensic of an unrooted mobile device. International Journal of Electronic Security and Digital Forensics. 2020; 12(1):118-137.
- Release notes (September 2019). UFED 4PC, UFED Touch 2, and UFED InField v7.23 https://cf-media.cellebrite.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/ReleaseNotes_7.23.pdf
- Press Release (December 2021). Oxygen Forensics Closes the year with Major upgrades in extraction capabilities, VPN support, Data analysis, and more. https://www.oxygen-forensic.com/uploads/press_kit/OFDv142ReleaseNotes.pdf
- Hazra S, Mateti P. Challenges in android forensics. In International Symposium on Security in Computing and Communication. 2017; 286-299. Springer, Singapore.
- Joshua J, Zach Lanier D, Mulliner C, Fora O, Ridley SA, Android’s GW. Hacker Handbook, John Wiley& Sons; https://books.google.co.in/books?id=2qo6AwAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q&f=false
- Gaikar V. Article by Tricks Machine on How to root samsung galaxy S3. 2012. https://www.tricksmachine.com/2012/07/how-to-root-samsung-galaxy-s3.html
- Kong J. Data extraction on mtk-based android mobile phone forensics. Journal of Digital Forensics, Security and Law2015; 10(4): 3.
- Alendal G, Dyrkolbotn GO, Axelsson S. Forensics acquisition—Analysis and circumvention of samsung secure boot enforced common criteria mode. Digital Investigation. 2018; 24: S60-S67.
- Tajuddin TB, Abd Manaf A. Forensic investigation and analysis on digital evidence discovery through physical acquisition on the smartphone. In 2015 World Congress on Internet Security (WorldCIS). IEEE. 132-138.
- Sathe SC, Dongre NM. Data acquisition techniques in mobile forensics. In 2018 2nd international conference on inventive systems and control (icisc). IEEE. 2018; 280-286.
- Ayers R. Smart Phone Tool Specification, computer forensic tool testing. 2010. https://tsapps.nist.gov/publication/get_pdf.cfm?pub_id=905497,www.cftt.nist.gov
- Osho O, Ohida SO. Comparative evaluation of mobile forensic tools. IJ Inf. Technol. Comput. Sci, 2016; 1:74-83.
Figures:
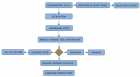
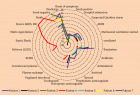
Figure 1
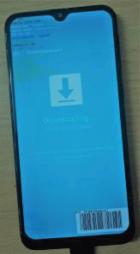
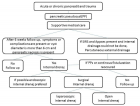
Figure 2
Figure 3
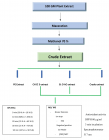
Figure 4
Figure 5
Figure 6

Figure 7
Similar Articles
-
Comparative analysis of mobile forensic proprietary tools: an application in forensic investigationParth Chauhan*,Tamanna Jaitly,Animesh Kumar Agrawal. Comparative analysis of mobile forensic proprietary tools: an application in forensic investigation. . 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001039; 6: 077-082
-
Analysis and Comparison of Social Media Applications Using Forensic Software on Mobile DevicesHüseyin Çakır*, Merve Hatice Karataş . Analysis and Comparison of Social Media Applications Using Forensic Software on Mobile Devices. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001065; 8: 058-063
Recently Viewed
-
Treatment Outcome in Patients with Myofascial Orofacial Pain: A Randomized Clinical TrialAnders Wänman*, Susanna Marklund, Negin Yekkalam. Treatment Outcome in Patients with Myofascial Orofacial Pain: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001046; 9: 001-008
-
Hygiene and Care Protocols for Implant-supported Dental Prostheses in Patients with DiabetesHakob Khachatryan, Emma Boshnaghyan, Sevak Papoyan, Gagik Hakobyan*. Hygiene and Care Protocols for Implant-supported Dental Prostheses in Patients with Diabetes. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001047; 9: 009-014
-
Advancing Oral Health and Craniofacial Science through Microchip ImplantsShekufeh Shafeie*. Advancing Oral Health and Craniofacial Science through Microchip Implants. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001048; 9: 015-018
-
Texture Analysis of Hard Tissue Changes after Sinus Lift Surgery with Allograft and XenograftMohammad Azimzadeh, Farzad Esmaeili, Narges Bayat, Kasra Rahimipour, Amir Ebrahimpour Tolouei*. Texture Analysis of Hard Tissue Changes after Sinus Lift Surgery with Allograft and Xenograft. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001049; 9: 019-022
-
Awareness and Knowledge of Specialists/Trainers and General Dental Practitioners about Medical-Related Osteonecrosis of the JawsAbdulhamit Taha Koca,Mustafa Bayhan,Yunus Ayberk Demir,Ayse Zeynep Zengin*. Awareness and Knowledge of Specialists/Trainers and General Dental Practitioners about Medical-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001050; 9: 023-031
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."