Abstract
Review Article
WMW: A Secure, Web based Middleware for C4I Interoperable Applications
Nida Zeeshan*
Published: 19 January, 2017 | Volume 1 - Issue 1 | Pages: 010-017
Modern-day enhancements in Enterprise Architectures (EA) has increased the interoperability issues in almost all domains; these issues are increasing day-by-day as organizations are spanning and information is being exchanged between different platforms. Command Control Computer Communication and Intelligence (C4I) complex systems are also facing the interoperability issues due to highly classified and sensitive information being exchanged. In this paper we have discussed the integration of different C4I applications running under heterogeneous platforms by allowing them to communicate using a secure and ciphered web based middleware named as Web Middleware (WMW). This middleware is a client-server based web adaptor to achieve clean, systematic, secure and reliable communication. The main feature among many is the simple HTTP browser based customization that do not require any specific or special add-ons and controls to be installed on the client machine. Architecture usage, and initialization of the WMW middleware is discussed with security and performance discussion.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001002 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Semantic interoperability; Enterprise architecture; Information exchange; Middleware; HTTP; Software engineering
References
- Alghamdi A, Siddiqui Z, Syed Quadri SA. A Common Information Exchange Model for Multiple C4I Architectures. Computer Modeling & Simulation (UKSIM). 2010; 538-542. Ref.: https://goo.gl/o4Niql
- Ghamdi A, Siddiqui Z. Common interoperability Framework for defense Architectures, A web Semantic Approach. 16th Internationa Conference on Distributed Multimedia Systems. 2010; 14-16. Ref.: https://goo.gl/IpDqt1
- Siddiqui Z, Abdullah A, Khan MK, Alghathbar K. Analysis of Enterprise Service Buses on Information Security, Interoperability and High-availability using Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) method. Physical Sciences. 2011; 6: 35-42. Ref.: https://goo.gl/MncrrU
- Siddiqui Z, Abdullah AH, Khan MK. Qualified Analysis b/w ESB(s) using Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) Method. International Conference on Intelligent Systems, Modelling and Simulation. 2011; 100-104. Ref.: https://goo.gl/F9M44P
- Siddiqui Z, Abdullah A, Khan MK, Ghamdi A. Node Level Information Security in Common Information Exchange Model (CIEM). College of Computer and Information Sciences. 2010; 21: 221-230. Ref.: https://goo.gl/rlZPma
- Patrick E. Information breifing to M&S CoC. Simulation-C4I Interoperability (SIMCI); Overarching IPT (OIPT). 2008.
- Tolk A. Beyond Technical Interoperability-Introducing a Reference Model for Measures of Merit for Coalition Interoperability. CCRTS. 2003; 47. Ref.: https://goo.gl/jIWlZS
- Dickerson CE. A Relational Oriented Approach to System of Systems Assessment of Alternatives for Data Link Interoperability. Systems Journal IEEE. 2013; 7: 549-560. Ref.: https://goo.gl/kCegpM
- Zenel B, Duchamp D. A general purpose proxy filtering mechanism applied to the mobile environment. ACM/IEEE. 1997; 248-259. Ref. https://goo.gl/D26blq
- Wetherall DJ, Guttag JV, Tennenhouse DL. ANTS: A Toolkit for building and dynamically deploying network protocols. IEEE OPENARCH. 1998. Ref.: https://goo.gl/F3SnOJ
- Kunz T, Black JP. An architecture for adaptive mobile applications. 11th International Conference on Wireless Communications. 1999; 27-38. Ref.: https://goo.gl/S4PJQD
- Liljiberg M, Alanko T, Kojo M, Laamanen H, Raatikainen K. Optimizing World-Wide-Web for Weakly connected mobile workstations: An Indirect Approach. 2nd International Workshop on Services in Distributed and Networked Environments. 1999; 32-139. Ref.: https://goo.gl/j9vp8M
- Buyukkokten O, Molina HG, Paepcka A, Winograd T. Power Browser: Efficient Web Browsing for PDA’s. Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. 2000; 430-437. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Sd1rH8
- Noble B. System support for mobile, adaptive applications. IEEE Personal Commu. 2000; 7: 44-49. Ref.: https://goo.gl/cbJDVR
- Villate Y, Gil D, Goni A, Illaramendi A. Mobile Agents for providing mobile computers with data services. DSOM 98. 1999; 1-12. Ref.: https://goo.gl/hQj4Yu
- Siddiqui Z, Abdullah AH, Khan MK, Alghamdi AS. Smart Environment as a Service: Three Factor Cloud based User Authentication for Telecare Medical Information System. Journal of Medical Systems. 2014; 38: 9997. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Klshmp
- Siddiqui Z, Abdullah AH, Khan MK, Alghamdi AS. Cryptanalysis and improvement of ‘a secure authentication scheme for telecare medical information system’ with nonce verification. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Application. 2016; 9: 841-853. Ref.: https://goo.gl/XlV89E
- Siddiqui Z, Alghamdi AS. SOA Based C4I Common-View Interoperability Model. Science International, Lahore. 2016; 26: 175-180. Ref.: https://goo.gl/VNW2Sj
- Siddiqui Z, Alghamdi AS. A Universal View SOA Interoperability Framework for Multiple C4I Applications. Science International, Lahore. 2016; 26: 97-100. Ref.: https://goo.gl/QLF5aC
Figures:
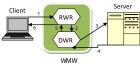
Figure 1
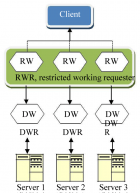
Figure 2
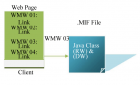
Figure 3
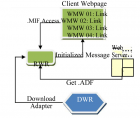
Figure 4
Figure 5
Similar Articles
-
WMW: A Secure, Web based Middleware for C4I Interoperable ApplicationsNida Zeeshan*. WMW: A Secure, Web based Middleware for C4I Interoperable Applications. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001002; 1: 010-017
Recently Viewed
-
Follow-up of patients with sarcoidosis in an internal medicine unit from a hospital in Asturias, Spain. Analysis of extrapulmonary manifestationsGómez de la Torre R*,Charca Benavente L,Yllera Gutiérrez C,Rolle V,Colunga Argüelles D. Follow-up of patients with sarcoidosis in an internal medicine unit from a hospital in Asturias, Spain. Analysis of extrapulmonary manifestations. J Child Adult Vaccines Immunol. 2022: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcavi.1001009; 6: 005-007
-
Application of Bioactive Cotton Packages for Packaging and Storage of Grains Using Aromatic ComponentsRefaie R,Zaghloul S,Elbisi MK,Hamdy A Shaaban*. Application of Bioactive Cotton Packages for Packaging and Storage of Grains Using Aromatic Components. Arch Food Nutr Sci. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.afns.1001064; 9: 011-019
-
Assessment of Albino Beech Supremacy to Pigmented Beech Proves to Be A Better Environmental Condition BioindicatorRenata Gagić-Serdar*,Miroslava Marković,Ljubinko Rakonjac,Goran Češljar,Bojan Konatar. Assessment of Albino Beech Supremacy to Pigmented Beech Proves to Be A Better Environmental Condition Bioindicator. Insights Biol Med. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.ibm.1001031; 9: 009-015.
-
Green Synthesis of Citrus sinensis Peel (Orange Peel) Extract Silver Nanoparticle and its Various Pharmacological ActivitiesJ Bagyalakshmi,M Prathiksha. Green Synthesis of Citrus sinensis Peel (Orange Peel) Extract Silver Nanoparticle and its Various Pharmacological Activities. Arch Pharm Pharma Sci. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.apps.1001065; 9: 009-013
-
The Accuracy of pHH3 in Meningioma Grading: A Single Institution StudyMansouri Nada1, Yaiche Rahma*, Takout Khouloud, Gargouri Faten, Tlili Karima, Rachdi Mohamed Amine, Ammar Hichem, Yedeas Dahmani, Radhouane Khaled, Chkili Ridha, Msakni Issam, Laabidi Besma. The Accuracy of pHH3 in Meningioma Grading: A Single Institution Study. Arch Pathol Clin Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.apcr.1001041; 8: 006-011
Most Viewed
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Evaluation of In vitro and Ex vivo Models for Studying the Effectiveness of Vaginal Drug Systems in Controlling Microbe Infections: A Systematic ReviewMohammad Hossein Karami*, Majid Abdouss*, Mandana Karami. Evaluation of In vitro and Ex vivo Models for Studying the Effectiveness of Vaginal Drug Systems in Controlling Microbe Infections: A Systematic Review. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001151; 6: 201-215
-
Prospective Coronavirus Liver Effects: Available KnowledgeAvishek Mandal*. Prospective Coronavirus Liver Effects: Available Knowledge. Ann Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acgh.1001039; 7: 001-010
-
Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian RandomizationYong-Qing Zhu, Xiao-Yan Meng, Jing-Hua Yang*. Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian Randomization. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001032; 7: 012-022
-
An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergiesNathalie Cottel,Aïcha Dieme,Véronique Orcel,Yannick Chantran,Mélisande Bourgoin-Heck,Jocelyne Just. An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergies. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001027; 5: 030-037

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."